Contents
Shapes and Solids
When you compare and contrast objects, you are in effect looking what makes them similar and different. This helps us to classify these objects according to their features, similarities and differences. In mathematics, we can classify objects as well. Here are several ways we can classify objects.
2-D Shapes
As a student you have to be able to classify shapes, notice features of shapes, and identify the shapes in real life.
Get familiar with shapes and build your own shapes.
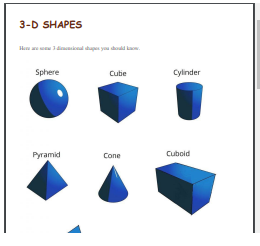
3-D Shapes
Look at these two tutorials as they show you how to make two simple shapes: a cube and a pyramid.
Click on the link below to download the PDF Worksheet below.

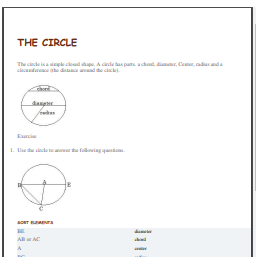
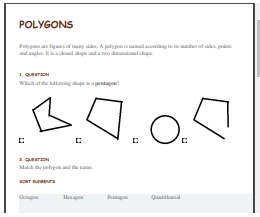
Polygons
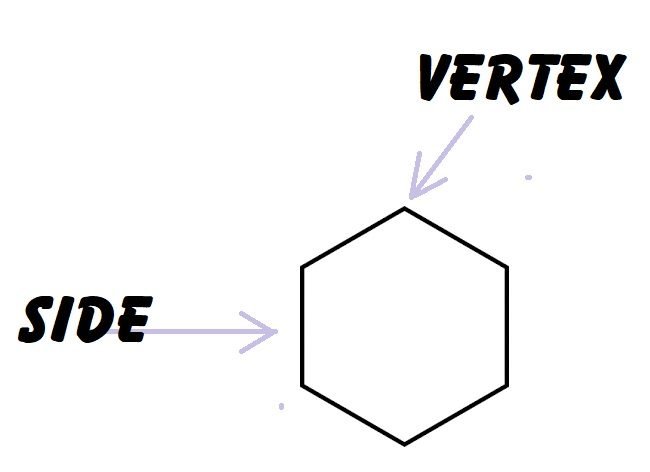
A polygon is a closed plane shape formed by three or more straight sides that connect to form a close shape. A polygon has edges or sides and points or vertices. Sides and vertices are the attributes or characteristics of a figure. Polygons don’t have round sides or any open line segments.
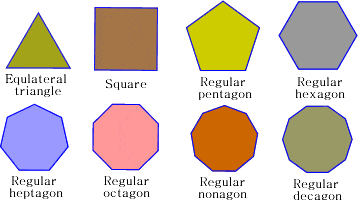
EXAMPLES OF POLYGONS.
They do not cross themselves.

Polygons are classified using attributes or characteristics. Shapes with three sides and three vertices are called triangles; shapes with four sides and four vertices are called quadrilaterals; and shapes with five sides and five vertices are pentagons.
Angles
An angle is a figure that is formed using two rays. The two rays meet at a common point. An angle is represented by the symbol ∠.
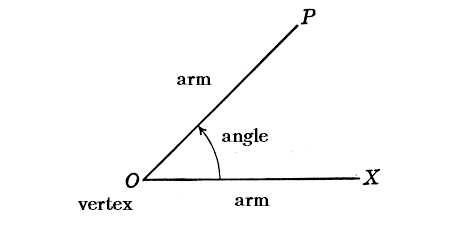
The figure below is formed from ∠POX. The two rays that form the angle are called arms: OP and OX form the arms of ∠POX. And so the end point of the angle is called the vertex. The vertex is ∠POX.
Now, observe the angle in the following.

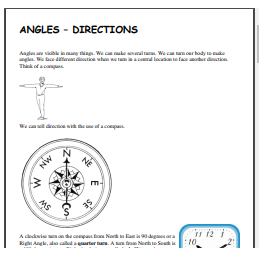
Can you spot angles in the things around you?
CLASSIFICATION OF ANGLES:
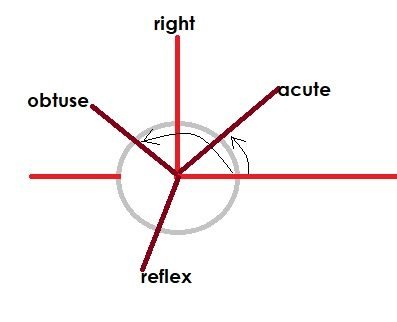
The following are angles according to their size. The diagram can help you remember the angles and their size.

- acute angles – measure less than 90°
- straight angles – measure 180°
- right angles – are exactly 90°
- reflex angles – measure more than 180°
- obtuse angles – is greater than 90 but less than 180°
- complete or full rotation – is exactly 360°
Angles could be seen within a shape or outside a shape. Angles within a shape are called interior angles and angles outside are exterior angles.

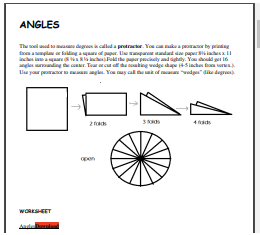
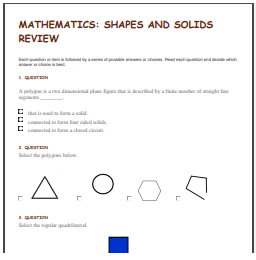
Worksheets
Click on the link below to download the PDF worksheets.
Click here for more worksheets.