On maps you see the various natural and man-made features on the earth’s surfaced. You have already come across some land forms already, such as continents and islands. Here are some more.
Summary:
Mountains
Mountains are huge chunks of rock that have been pushed up out of the earth. Some mountains stand alone, but most are connected together in long chains called mountain ranges. Some mountains are bare and rocky, while others have green forests and fields of grass growing on their sides. Some have snow on the tops all year round.

Trinidad has three mountain ranges: the Northern, central and Southern ranges. The Northern range is the highest with El Cerro del Aripo (picture above) which is 3,085 ft (940 m) tall. Another tall mountain is El Tucuche (reaching 3000 ft. or 900 m). There sides are covered with a tropical rainforest. Tobago has a central mountain range called the Main Range which rises to 1,890 feet.
In order to measure the height of a mountain, you start from the land it is sitting on. It starts at where the land begins, at the top of the sea. This type of measurement is measuring at sea level. All the land in the world is either above or below sea level

Hills
A hill is land raised that has sloping sides. Hills may be small and flat to high and rolling.The tallest hills in Trinidad are Mount Tamana (307 m), Mount Harris and Brigand Hill, are all located in the northerneastern portion of the range.
Volcanoes
A volcano is a a special kind of mountain made of red-hot rock that pours up out of the earth. Magma contains dissolved gases. It rises to the opening and pours out. When magma pours out of a volcano, it is called lava.
The lava is thick as syrup or as thin as watery soup, but it cools into a black, gritty rock. This rock builds the volcano. The rock that pours out piles up and form a cone or dome, with a tunnel running down its middle. Some volcanoes sit quietly for hundreds or thousands of years. Some may suddenly become active and shake the earth.
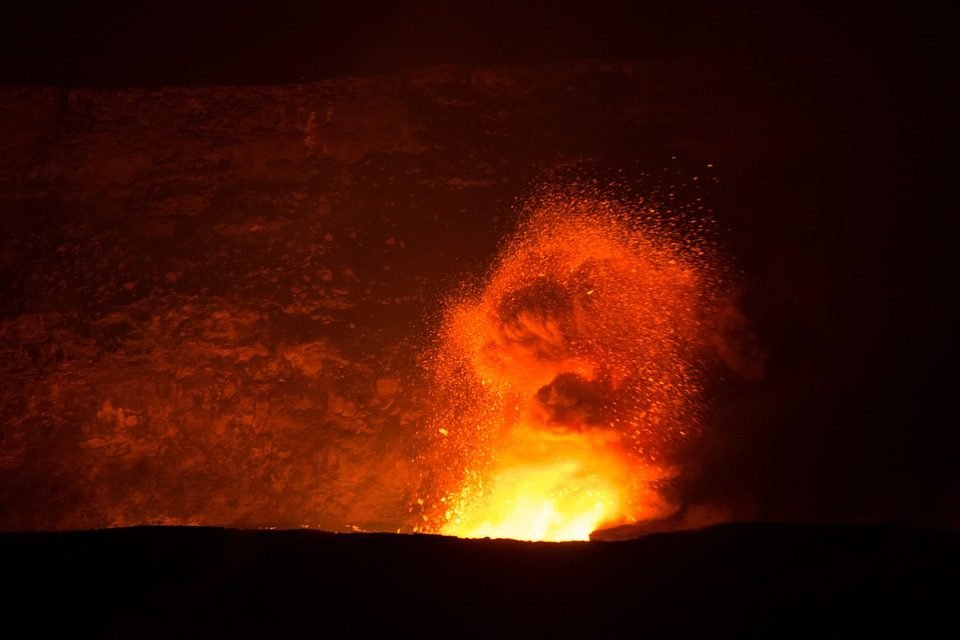
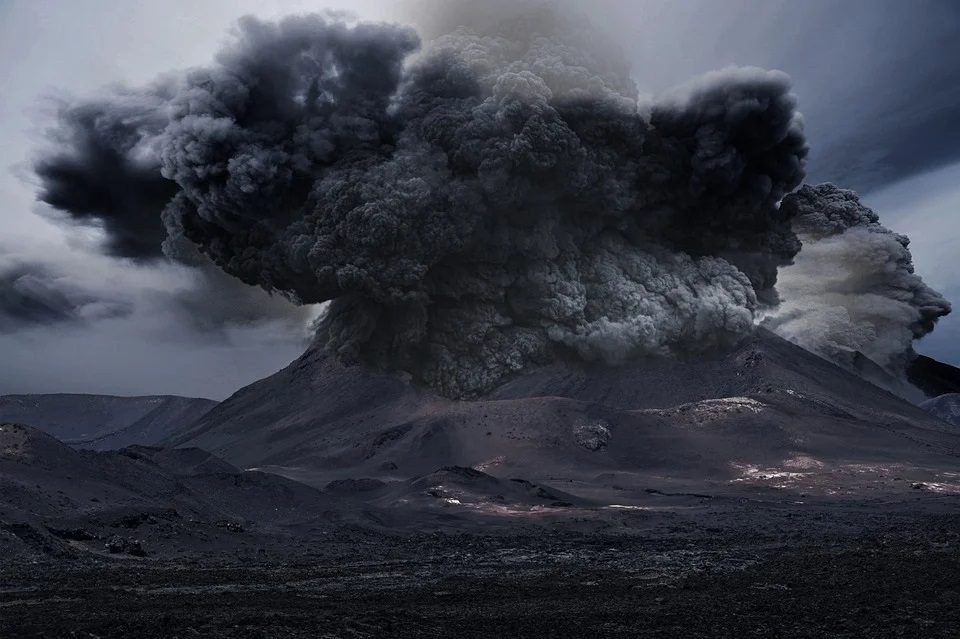
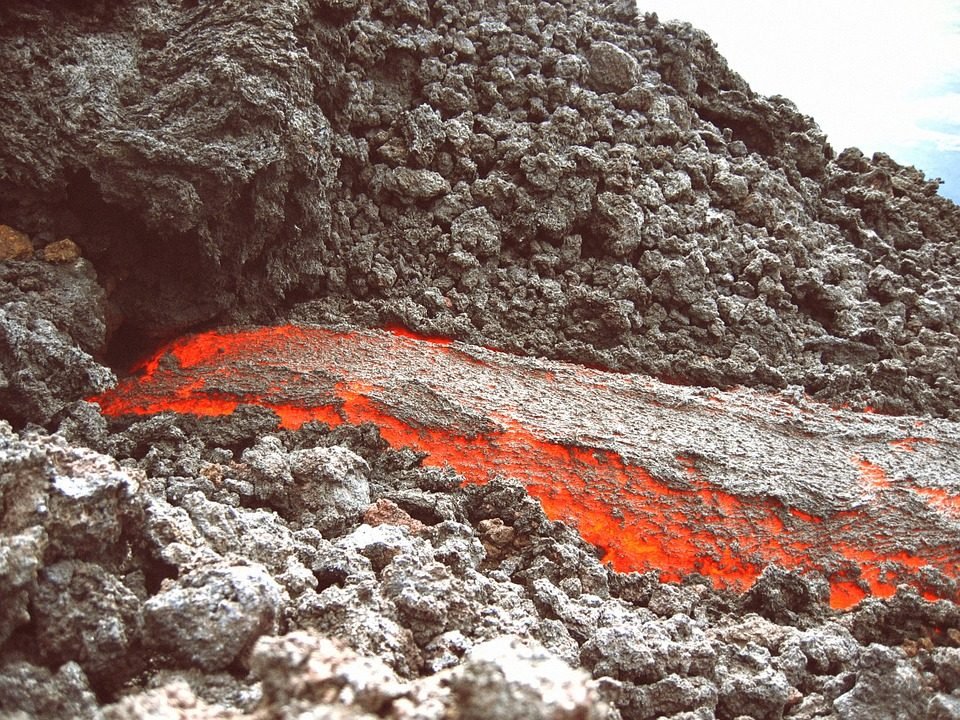



There are thousands of volcanoes in the world. Some are “dead” (they are not active). Though volcanoes can kill many people or destroy villages or cities, they have been known to do some good. The ash from a volcano is rich and contribute to most fertile soil in the world.
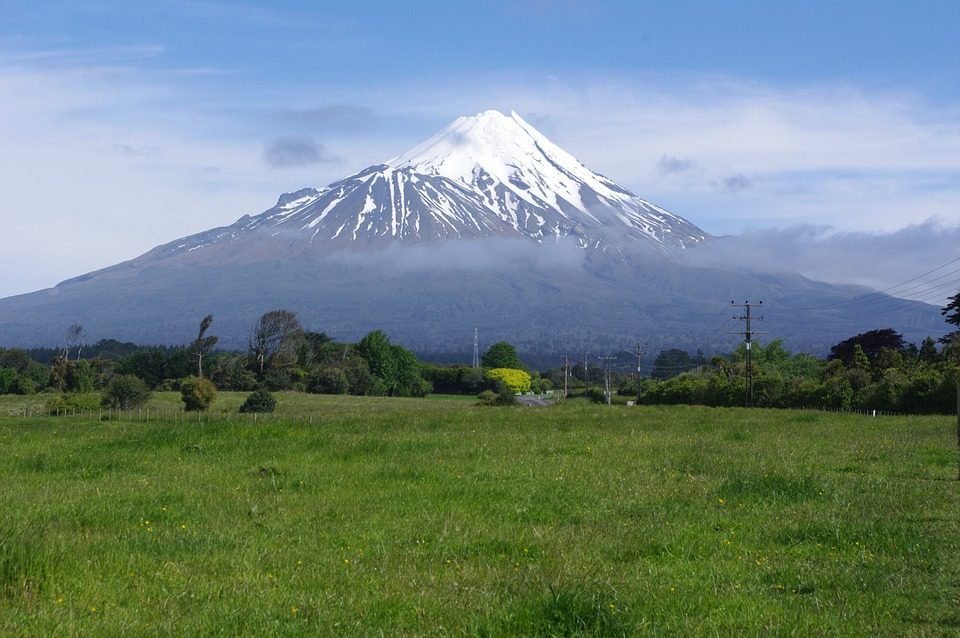

In the Caribbean, the volcanoes are manly steep-sided and conical in shape. There are 19 “live” (volcanoes likely to erupt) in the Eastern Caribbean. Every island from Grenada to Saba can have a possible volcanic eruption. Such islands are: Grenada, St. Vincent, St Lucia, Martinique, Dominica, Guadeloupe, Montserrat, Nevis, St. Kitts, St. Eustatius and Saba. And the other islands: Anguilla, Antigua, Barbuda, Barbados, British Virgin Islands, most of the Grenadines and Trinidad and Tobago are subject to volcanic dangers: ash fall, and volcanically-generated tsunamis.
You will notice that most of the volcanoes in the islands are called Soufriere. The term is French and means Sulphur, which is naturally deposited at the surface by volcanic gases.(Learn more about volcanoes in the Caribbean, click here.)
Recently this year (2021) the Soufriere volcano of St. Vincent erupted. It has created a crisis on the island where 110,000 inhabitants live. About 20000 inhabitants had to be evacuated from their homes. The last time this volcano erupted was 1979. Now it has been active since April 9, letting out clouds of ash and smoke.
We know this incident will have a medium and long term impact on St Vincent and its neighbouring islands: Barbados, Antigua and Barbuda, and others. The impact is not only from volcanic ash but tourism will be impacted even more since we are under restrictions due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Mud Volcanoes
A mud volcano is a mud dome create by the eruption of mud or slurries, water and gases. They are not true igneous volcanoes. They do not shoot out lava. They are in places where natural gas is present.
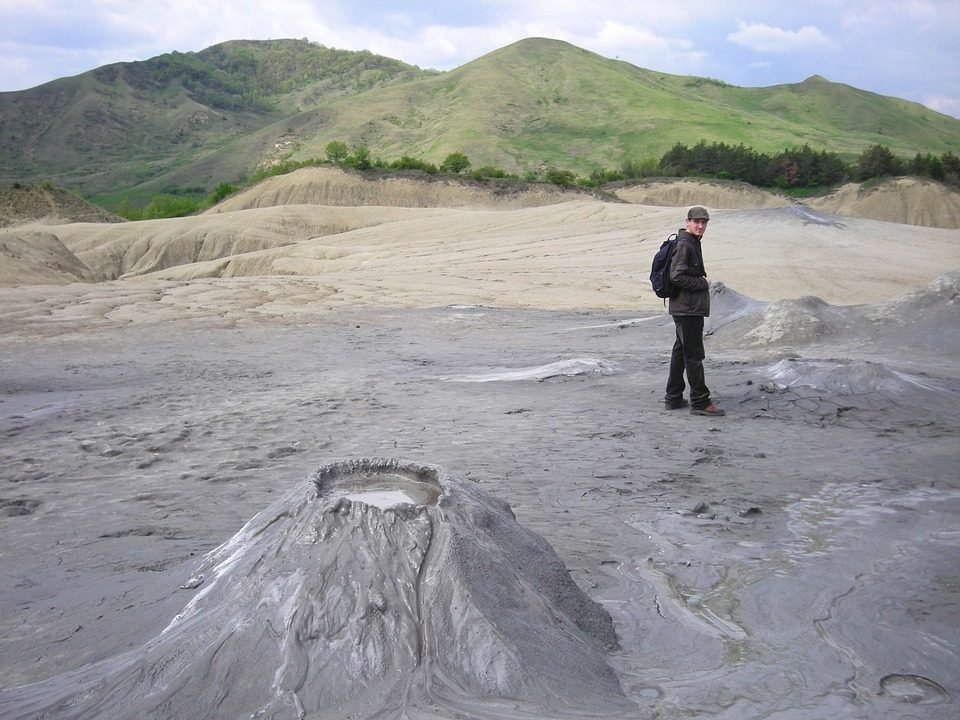

Valleys
Nature creates ditches. A valley is a long ditch. A valley is a low area between hills or mountains. Most valleys are made by rivers or streams.. Valleys can be formed by the earth’s movement also . A valley has sides, or valley walls and a floor. A valley may have a V-shaped ditch or U-shaped ditch.



Plains
There are many great flat places where the land levels and gently rolls out for miles. These flat places are called plains. All over the world there are great flat plains.
All over the world there are great flat plains.

In Trinidad, The Caroni Plain is a lowland area between the Northern Range and the Central Range.The lowland areas in the south of the central range are the Naparima Plain on the west and the Nariva Plain on the east. The Caroni plain was a major region of sugar and cocoa production.
Desert
A desert is a barren area of where there is little precipitation. There are many different kinds of deserts. Some are rolling, sandy places where hardly a plant may grow.

Some are flat plains that may be covered with many kinds of plants. Sahara is the hottest desert. It also has patches of trees and grass. Patches of greenery is called oasis.

The hottest desert recorded a temperature of 136 degrees Fahrenheit (58 degrees Celsius).



Deserts could be hot all year round. Others could be cold in the winters. When it does rain in a desert, sometimes it is so hot that the rain dries up before it reaches the ground.
Dunes
Dune is a large of wind-blown sand. Most common in deserts and near beaches.


Plateaus
Plateau (plural is plateaus or plateaux) is a high plain or a tableland. It is a relatively flat terrain raised above the surrounding area. Plateaus can be formed by a by volcanic lava or the upward movement of the Earth’s crust.



A valley could form when the river water cuts through the plateau.
Swamps
A swamp is an area of land that is continually saturated or filled with water. Swamps are a type of wetlands and can be fresh water and saltwater. Other types of wetlands are marshes, bogs and fens.
Freshwater swamps, commonly inland, form along large rivers or lakes. Saltwater swamps are found along tropical and subtropical coastlines. Swamps are dominated by woody plants and trees, but are neither totally land or totally water.

In Trinidad we have the Caroni Swamp and Nariva swamp. They are freshwater swamps in Forested areas.
Rivers and Streams
A river is a large flowing body of water that usually empties into a sea or ocean. A river may begin as a trickle of melting snow or underground water. It winds down a mountainside along rocks. It widens as it meets other trickles until it forms faster-moving streams. The moving water, soil and stones cut a groove into the mountainside. As more trickles joins, it widens and the river becomes more rapid.
The Ortoire river is the longest river in Trinidad. It is over 55 km in length. The river is known for giving off a blue light every 10 years. The bioluminescence of living organisms living in the water causes this blue light.
The bottom of the river is called the bed and the sides the banks. Where the mountainside ends is the cliff and the rushing river rushes out over the cliffs and falls. This fall is called the waterfall.
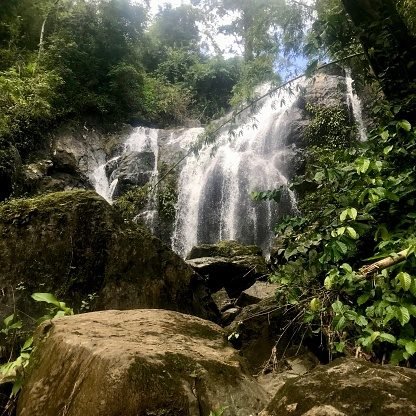


Avocat Waterfall in Blanchisseuse, Trinidad is a popular waterfall. It falls at 50 feet into a pool. Another, Maracas Waterfall is Trinidad’s highest waterfall, falling at an altitude of about 300 feet.
At the bottom of the waterfall the land slopes very gently and so the river moves more slowly.
The river flows out across plain and out towards the distant sea.
Delta
The delta is the place where a river ends, where it flows into a lake or the sea. This is the mouth of the river. Can you guess the name for where the river begins? If you said the head, you are right!
The river carries with it sand and soil. Most of the sand and soil settles at the the river mouth during low tide. It piles up in riverbed and a kind of island is forms in the middle of the river mouth. The river now has two branches that flows into the sea. In time the islands get larger and more branches forms. Over time there is a great plain at the river mouth; it is usually shaped like a triangle. Hence the name delta which is a Greek letter in the alphabet called delta (uppercase/lowercase Δ δ) .

Lakes or Ponds
Lake or a pond is water that has land all around it. Unlike ponds, lakes have to be a significant size in order to be called a Lake.

Most lakes are just holes in the ground filled with water. Lakes are formed by holes dug by glaciers, when the earth cave in leaving a hole, where part of a river becomes a lake, or the crates of dead volcanoes.
Glaciers
A Glacier is a persistent body of dense ice. Glacial lakes typically form at the foot of a glacier. As the glaciers move and flow they form grooves in the land. It fills up and form lakes.

Underground Lakes
An underground lake is a lake under the surface of the earth.

River Lakes

Crater Lakes

Ocean
The ocean is a huge body of saltwater that covers the earth’s surface. The ocean covers about 71 percent of the Earth’s surface. The one global ocean is divided into distinct geographic regions: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic Oceans, and the Southern Ocean.

Coast
Coast or coastline the part of the land adjoining or near the sea or ocean. Coastlline changes as the land shrink or grow through erosion, deposits and erupting volcanoes.
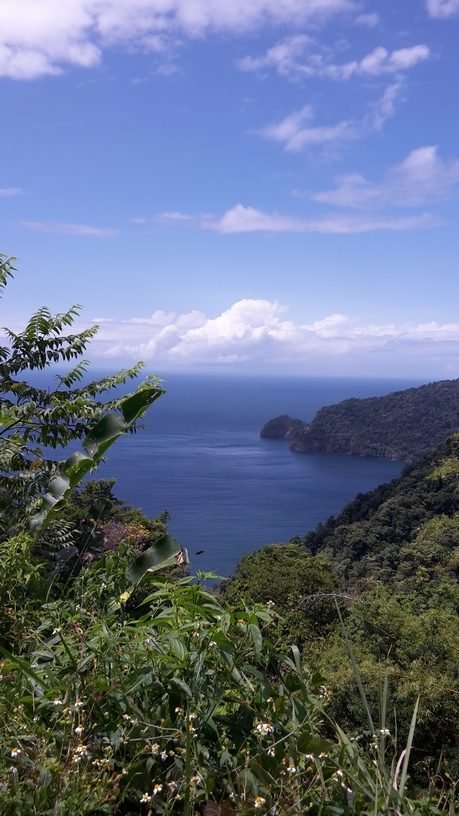

Bay
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake or another bay. A bay can be large or small. It is different from a gulf. A gulf goes inland, it is larger and a bay has a much smaller opening.
List of Bays in Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad:
Macqueripe Bay
Blanchisseuse Bay
Mayaro Bay
Carli Bay
Paria Bay
Cocos Bay
Parlatuvier Bay (Tobago)

View of Columbus Bay
A peninsula is a a body of land that is surrounded by water on three sides that are connected to a mainland.

Archipelago
An Archipelago is an extensive group of islands, sometimes called an island group or island chain. Island is a piece of land surrounded by water.
3 Archipelagos in the Caribbean:
- Greater Antilles
- The Lesser Antilles
- The Lucayan Archipelago ( or Bahama Archipelago, is an island group comprising of The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands).

Isthmus
An isthmus is a strip of narrow land with water on each side, connecting two greater land masses. The Isthmus of Panama connects the North and South America and the Isthmus of Suez connects Africa and Asia. These two isthmuses are bisected by canals and used for shipments.

Note, a canal such as the one above is a lot different from a strait.
A strait is a naturally formed waterway that connects two larger bodies of water. It is commonly a channel of water that lies between two land masses.

Reefs
A reef is a ridge of jagged rock, coral, or sand just above or below the surface of the sea. Coral reefs come in a many shapes and colours. Corals belong to the phylum cnidaria (the same in which jellyfish, anemones, etc. also belongs). They feed on small marine life, such as fish and plankton.

Types of Landforms Videos
Videos 1: Mountains, Hills, Valleys, Desert, Plains, Plateaus
Worksheets
Click the links below to download the PDF worksheets.