Summary
What are Habitats
Habitats are places where plants and animals live. They are natural environments where the species of the earth live, find food, shelter, protect themselves and reproduce. Habitats have physical and biological features.
Definition: A habitat is the natural environment of an organism, type of place in which it is natural for it to live and grow. A habitat offers an organism a home where the right conditions exists for it to survive, eat and reproduce. The plants get the right combination of light, air, water and soil.
Learn more about how living organisms live on rotten logs. Click here.


World Habitat Day
The United Nations designated the first Monday of October of every year as World Habitat Day to reflect on the state of our towns and cities, and on the basic right of all to adequate shelter.
Activity: Walk around your home and observe the wildlife around you in their habitat.
Colouring Sheets

Categories of Habitats
There are five major biomes, areas with similar characteristics, found in the world. These five types of habitats are aquatic, desert, forest, grassland, and tundra.
Terrestrial habitat types include forests, grasslands, wetlands and deserts. Each vary in climate, temperature, soil, and vegetation types. Each have its own typical communities of plants and animals.
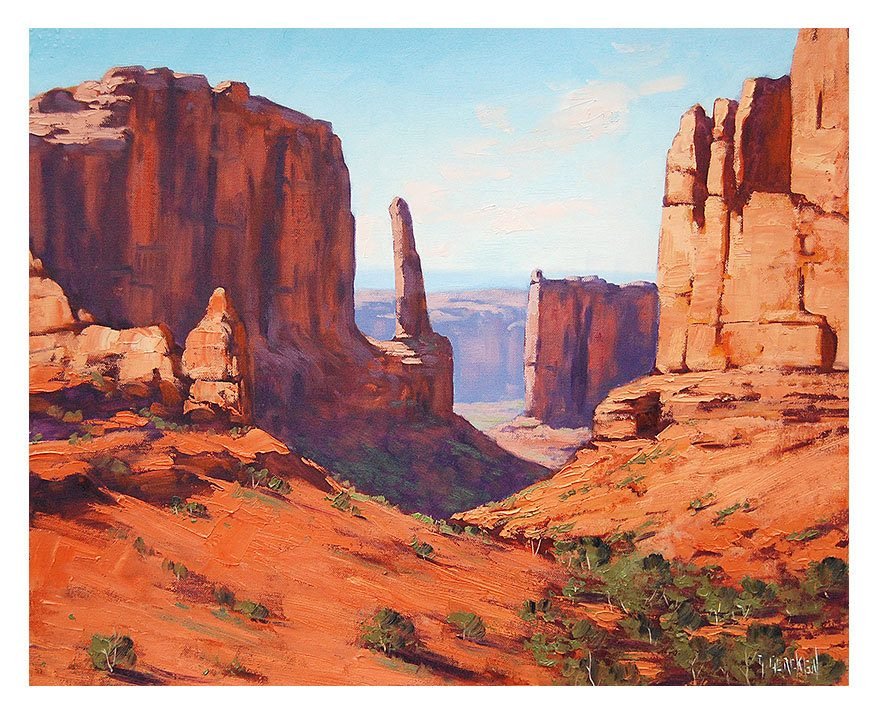

Deserts are the driest areas on earth.
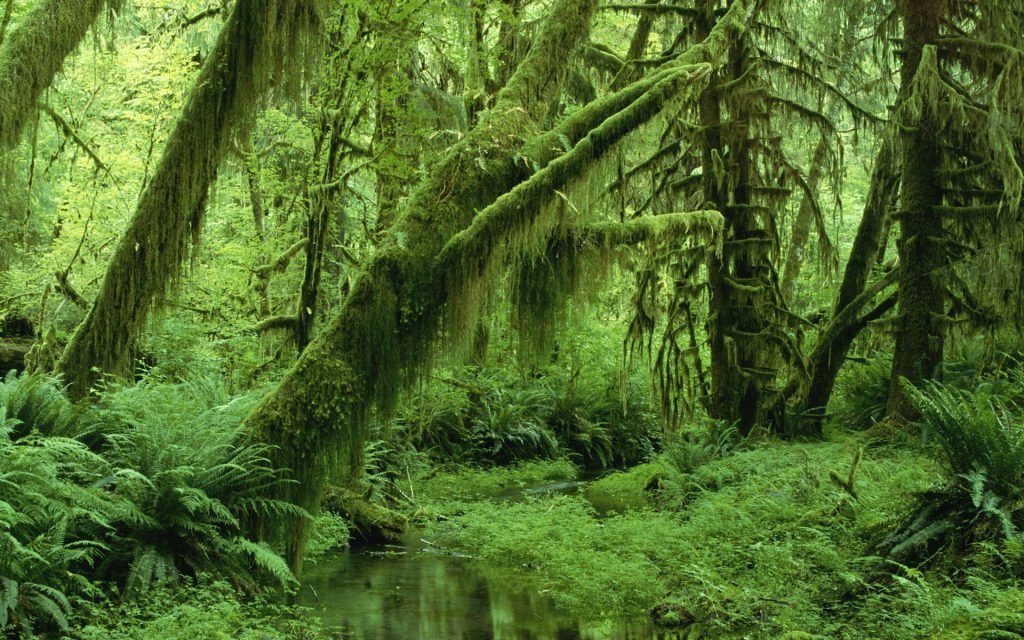

There are different types of forests, such as temperate and tropical.


Aquatic biome includes the seas and oceans, lakes and rivers, wetlands and marshes, lagoons and swamps, mangroves, slat marshes, and mud flats.
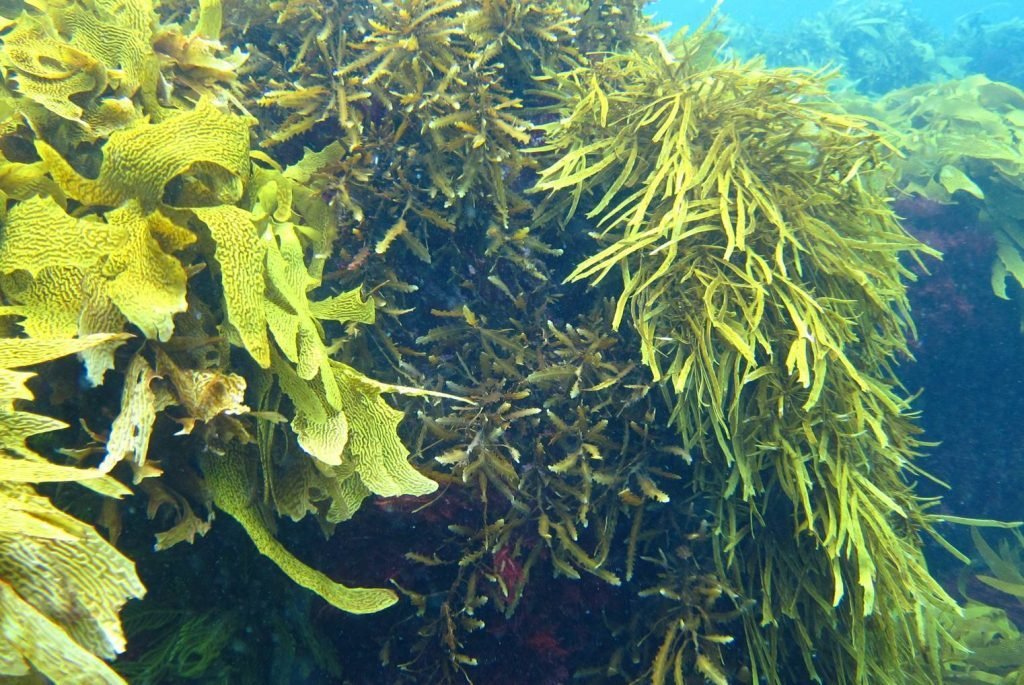


Learn more about habitats. Click on this link.
Picture source
Habitat changes
All parts of the ecosystem are connected. One part changes, and it affects the rest of the system. Each part of the habitats are generally not always the same.

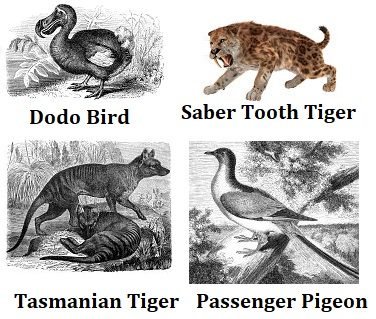
Some species disappear, and others take its place.
Here is a video about one of the above animals, the Tasmanian Tiger.

Note: Biodiversity – describes the many different species that share one habitat.
When biodiversity is threaten, there you will see the effects on the environment. Habitats change over time. Some main causes are:
- A violent event;
- Gradual changes that occur over millennia such as climate change;
- Weather pattern changes;
- Human activities cause changes; and
- The introduction of alien species can have devastating effect on native wildlife.


Below is a video on factors that cause changes in a habitat. Take your notes.

Is it Worth Saving the Species?
Discussion question
Observe a habitat close to you. Review the essential components of the habitat: food, water, shelter, and space. How have human activity affect it?
Protecting Habitats
It is important to protect habitats. The lost of a habitat could be tragic. This threatens species diversity. Human activity, on the most part, can destroy, fragment or degrade a habitat. The main causes for habitat loss are:
- logging forests,
- oil and gas exploration and development,
- draining swamps and coastal habitats for development,
- road construction,
- cattle ranching,
- mining,
- pipelines,
- damming rivers and draining them for irrigation, and
- urban sprawl,
When a habitat is affected in such a way, it cannot provide the protection and needs that a species need to survive, live and raise their young. Affected habitats also threaten the future of humanity.




Humans threaten the ecosystem by being wasteful.

Protecting Habitats
One way of protecting habitats is by being frugal. We can hold on to somethings a little longer. To this, effort must be place on everyone being resourceful, producing and using products that last a lot longer.
Some more ways are:
Participate in a local trash clean-up to help protect the habitats of endangered species and wildlife.
Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle

Plant native flowers, trees and bushes in your backyard.

Leave wildlife animals alone! Do not remove them from their environment. These animals survive best in their own habitat.

Be an educated Consumer

Never buy exotic animals, especially caught in the wild.
Support genuine effort for ecotourism, photo safaris, or community-based humane education programs.

Picture source
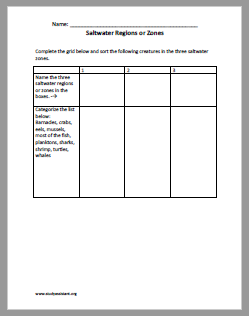
Aquatic Habitats
An aquatic habitat is a habitat with water. It includes areas that are permanently covered by water and surrounding areas that are occasionally covered by water.

The water in the estuary contains small pieces of plants, detritus (waste or debris of any kind), microscopic organisms, and algae in the water. Water is more salty closer to the sea, less salty as you move up the river. Salt in the water makes the water heavier than freshwater. This is why it is easier to float in ocean water than a lake. At the bottom of an estuary, the soil or mud is thick and deep. Small organisms live and breathe in the top layers of mud, which contains some oxygen. Many plants live in different parts of the estuary. Some plants grow in marshes, their roots grow in the mud, and the stem submerged when the tide comes in.

Notes on Surface and Ground Water

Natural events affect aquatic environments.
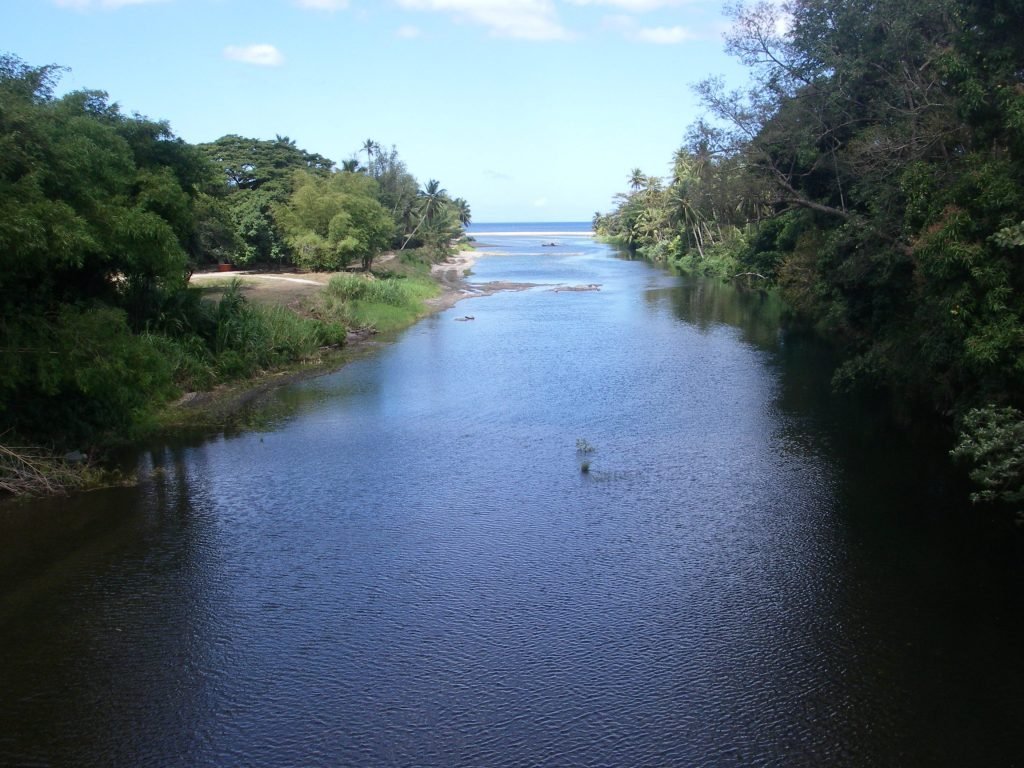

Tides affect salinity (amount of salt ). Rising levels of ocean water at the shore pushes more saltwater up into the estuary and river. During low tide, ocean water draws back from the estuary.
Flooding causes the estuary to get more freshwater from the river. When a river floods it deposits nutrient rich sediment on the banks, bits of vegetation washes into the water and become food for aquatic organisms. Floods replenish lakes and ponds, it raises the water table.

Flood through extreme events can be detrimental to aquatic system until balance is reached.

Human Activities affect aquatic environments.
Human activities affect aquatic environment in the most disruptive way.

These activities affect the water cycle, interferes with the level of streams and flow of water, drain wetlands, and eliminate aquatic organisms. Some of these activities uses a lot of our water resources such as oil sands and mining.

When people build dams, they change freshwater ecosystems from a flowing system into a still system.

All life is made of water and needs water. Water is our most threaten resource. The decreasing amounts and polluted, unsafe water is leading to sickness and death. This is the most important reason we should protect our aquatic habitats and all habitats.
Learn more of this under the topic of ecosystems and cycles.

Discussion
Make a list of things that live in estuaries and rivers. Discuss how a few of these things would fare if the water they live in was saltier, or if there was a flood. Go to the CHAT. Click on the link below.

Suggested Activity
Essay: Write a short paragraph explaining why you think it is important to save Earth’s Coral reefs.
Worksheets
Click on the links below to download the PDF worksheets.